Abstract
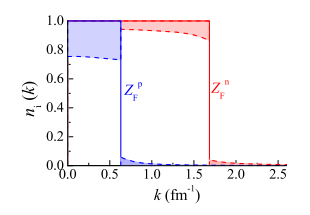
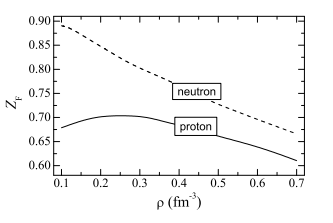
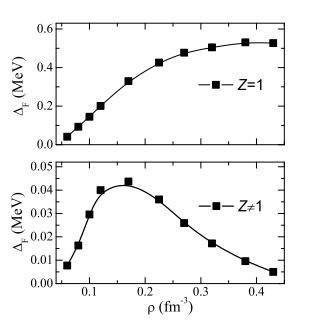
The Fermi surface depletion of beta-stable nuclear matter is calculated to study its effects on several physical properties that determine the neutron star (NS) thermal evolution. The neutron and proton Z factors measuring the corresponding Fermi surface depletions are calculated within the Brueckner-Hartree-Fock approach, employing the AV18 two-body force supplemented by a microscopic three-body force. Neutrino emissivity, heat capacity, and in particular neutron (PF2)-P-3 superfluidity, turn out to be reduced, especially at high baryonic density, to such an extent that the cooling rates of young NSs are significantly slowed.
 |  |  |
DOI:10.3847/0004-637X/817/1/6
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.02746.pdf