Abstract
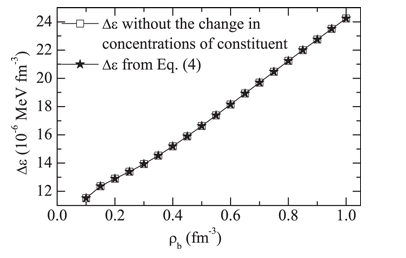
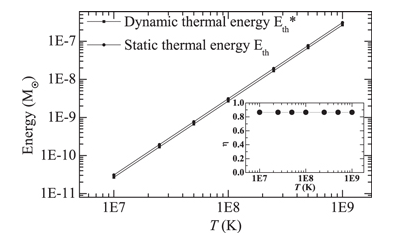
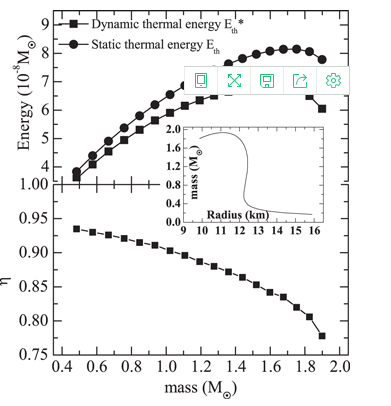
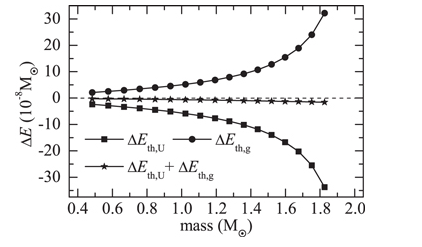
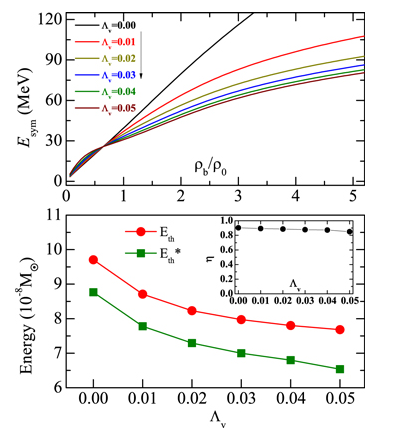
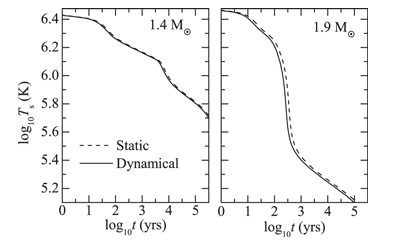
The observations combined with theory of neutron star (NS) cooling play a crucial role in achieving the intriguing information of the stellar interior, such as the equation of state (EOS), composition and superfluidity of dense matter. The traditional NS cooling theory is based on the assumption that the stellar structure does not change with time. The validity of such a static description has not yet been confirmed. We generalize the theory to a dynamic treatment; that is, continuous change of the NS structure (rearrangement of the stellar density distribution with the total baryon number fixed) as the decrease of temperature during the thermal evolution, is taken into account. It is found that the practical thermal energy used for the cooling is slightly lower than that is estimated in static situation, and hence the cooling of NSs is accelerated correspondingly but the effect is rather weak. Therefore, the static treatment is a good approximation in the calculations of NS cooling.
 |  |  |
 |  |  |